Introduction
As cannabis continues to gain legal and social acceptance around the world, the conversation around medical marijuana and recreational cannabis has become more nuanced. While both come from the same plant, their purposes, compositions, and regulations are vastly different. Understanding these differences is crucial for patients, healthcare professionals, and anyone curious about how cannabis is reshaping modern medicine.
Medical marijuana is more than just a cultural trend — it’s a legitimate therapeutic option supported by growing scientific evidence. From pain relief to seizure control, its benefits have transformed treatment for many chronic conditions. But how does it differ from recreational cannabis? Let’s explore the science, legality, and medical realities behind both.
What Is Medical Marijuana?
Medical marijuana refers to cannabis or its chemical compounds (primarily THC and CBD) used to treat or manage specific health conditions under medical supervision. It’s prescribed by licensed physicians and dispensed through regulated medical channels.
Unlike recreational cannabis, medical marijuana is developed with precise ratios of cannabinoids to target symptoms effectively while minimizing psychoactive effects. For instance, a patient with chronic pain may be prescribed a high-CBD, low-THC strain to relieve discomfort without feeling “high.”
Regulations differ worldwide. In the United States, over 30 states permit medical marijuana use with a valid prescription. In Australia and Canada, it’s tightly regulated and available only through licensed healthcare providers.
See more: Exploring the Role of Medical Cannabis in Cancer Treatment
How Cannabis Works in the Human Body
The therapeutic effects of cannabis come from its interaction with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) — a complex cell-signaling network that helps regulate pain, mood, sleep, and immune response.
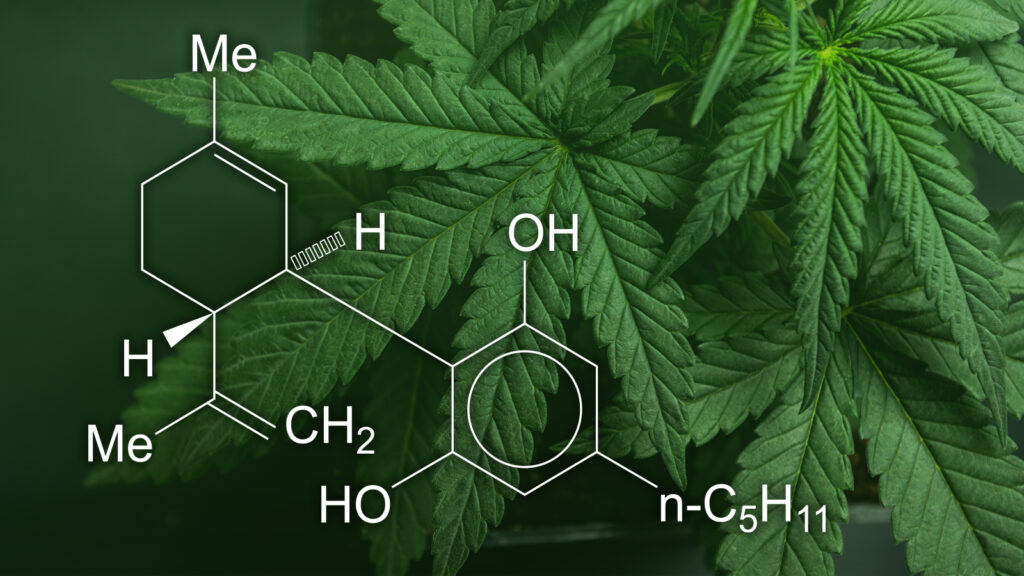
Cannabinoids like THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) bind to specific receptors (CB1 and CB2) in the body, influencing various physiological functions.
- THC primarily affects CB1 receptors in the brain, leading to euphoria or relaxation.
- CBD interacts more with CB2 receptors in the immune system, providing anti-inflammatory and calming effects without intoxication.
This interaction helps explain why cannabis can relieve pain, reduce anxiety, and even assist in neurological disorders like epilepsy and multiple sclerosis.
Key Medical Uses and Benefits
Medical marijuana is increasingly recognized for its ability to alleviate symptoms of chronic and debilitating conditions. Some of the most common medical uses include:
- Chronic pain management: Patients with arthritis, fibromyalgia, or neuropathic pain often find relief through cannabis-based products.
- Epilepsy: FDA-approved CBD formulations, like Epidiolex, have shown remarkable success in treating severe childhood epilepsy syndromes.
- Cancer-related symptoms: Cannabis can reduce nausea and vomiting from chemotherapy and stimulate appetite in cancer or HIV patients.
- Mental health conditions: Studies suggest potential benefits for PTSD, anxiety, and insomnia — though medical supervision is essential.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Early research indicates that cannabinoids may protect brain cells in conditions like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
In one notable case, an Australian veteran suffering from PTSD reported improved sleep and reduced anxiety after a controlled medical cannabis regimen, demonstrating its real-world therapeutic potential.
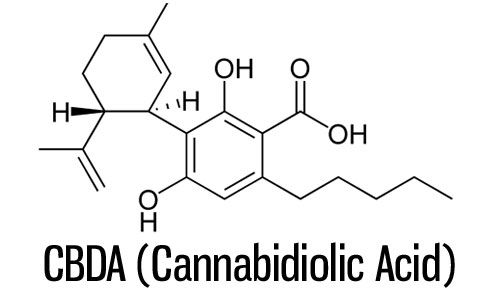
The Role of Cannabinoids: CBD and THC
The two primary cannabinoids, CBD and THC, define the difference between medical and recreational cannabis.

- CBD (Cannabidiol): Non-psychoactive, known for reducing inflammation, pain, and anxiety. It’s often used in oils, capsules, and topical creams.
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol): Psychoactive compound responsible for the “high” sensation. In medical use, it helps with pain relief, nausea, and muscle spasticity.
Medical marijuana often features a balanced CBD-to-THC ratio, depending on the condition being treated. Recreational cannabis, however, typically prioritizes higher THC levels for stronger euphoric effects.
Medical Marijuana in Modern Treatments (Real-World Examples)
In Canada, medical cannabis has been legal since 2001 and is now integrated into mainstream healthcare. Patients can obtain products through government-approved suppliers with a prescription.
In the United States, institutions like Johns Hopkins University and Mayo Clinic are researching cannabis’s potential to reduce opioid dependency. Meanwhile, Australian clinics are prescribing medical cannabis for chronic pain, epilepsy, and palliative care — showing the global shift toward legitimizing its use.
For example, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) reported that over 370,000 medical cannabis prescriptions were issued in 2023 — a sharp rise that reflects growing patient confidence and physician awareness.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The legal landscape surrounding cannabis is complex and varies by region.
- Medical marijuana is legal in many countries under strict regulation, requiring a doctor’s approval and controlled distribution.
- Recreational cannabis remains illegal or restricted in most places due to concerns about misuse and safety.
Ethically, the conversation centers on accessibility and stigma. Many patients still face challenges obtaining legal prescriptions or fear social judgment. As laws evolve, ensuring fair access to cannabis-based treatments is becoming a major policy priority.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While generally safe under medical supervision, cannabis isn’t without risks. Common side effects include:
- Drowsiness or fatigue
- Dry mouth
- Short-term memory issues
- Dizziness or mild anxiety
Long-term overuse — especially with high-THC products — may lead to dependency or cognitive impairment. That’s why medical guidance is crucial for dosage, strain selection, and monitoring side effects.
The Future of Cannabis in Medicine
As global research accelerates, cannabis is poised to play an even bigger role in modern healthcare. Advances in cannabinoid-based pharmaceuticals, nanotechnology delivery systems, and personalized cannabis therapy are transforming how doctors treat chronic conditions.
Countries like Germany and Australia are expanding clinical trials, while the U.S. FDA continues to evaluate new cannabis-derived medications. The future looks promising — with growing acceptance that cannabis, when used responsibly, can complement conventional medicine.
Conclusion
Medical marijuana and recreational cannabis may share roots, but their paths diverge sharply in purpose and practice. Medical marijuana focuses on healing, symptom control, and improving quality of life — all under regulated medical guidance. Recreational cannabis, on the other hand, is primarily for enjoyment and relaxation.
As research deepens and laws continue to evolve, understanding this distinction empowers patients and professionals to make informed, responsible decisions about cannabis use in healthcare.
FAQS
Medical marijuana is prescribed to manage chronic pain, anxiety, epilepsy, and chemotherapy-related nausea. It helps patients reduce opioid dependency and improve their quality of life when used under medical supervision.
No. Medical marijuana is used under prescription with regulated cannabinoid levels, while recreational marijuana is consumed for leisure and often has higher THC content.
Yes. Side effects may include dizziness, fatigue, or impaired short-term memory. However, when prescribed properly, it’s generally safe and effective for chronic conditions.
Patients must consult a licensed healthcare provider, obtain a prescription, and purchase from authorized dispensaries. Regulations differ by state and country.
CBD is non-psychoactive and treats anxiety and inflammation, while THC causes euphoria but offers potent pain relief. Both are medically valuable in the right doses.